Listen to the article
The rapid evolution of online social networks (OSNs) over the past decade has fundamentally transformed how people consume news and information worldwide. Platforms like Twitter, Facebook, Instagram, and WhatsApp have steadily displaced traditional print media, creating new patterns of information consumption and sharing.
What began as simple platforms for personal updates and social connections has morphed into sophisticated ecosystems where news travels at unprecedented speed. These networks now serve as primary sources of information for billions of users globally, allowing real-time responses and feedback on local and international topics.
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated this shift dramatically, as lockdowns and social distancing measures drove more people online. During this period, social networks became lifelines for information during rapidly changing social, economic, and health developments.
However, this transformation has brought significant challenges. The proliferation of false information—whether shared unintentionally or created deliberately for propaganda purposes—has emerged as a major concern for platform operators, governments, and users alike.
“The line between legitimate news and misinformation has become increasingly blurred on social platforms,” explains a recent study highlighting the need for better detection systems. “When users unknowingly share fake news believing it’s true, it creates a dangerous cycle of misinformation.”
While numerous machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) applications have been developed to combat this problem, most remain at the experimental level. Many existing studies focus more on algorithm performance than on practical user applications, often using limited datasets that don’t reflect the true scale and complexity of the problem.
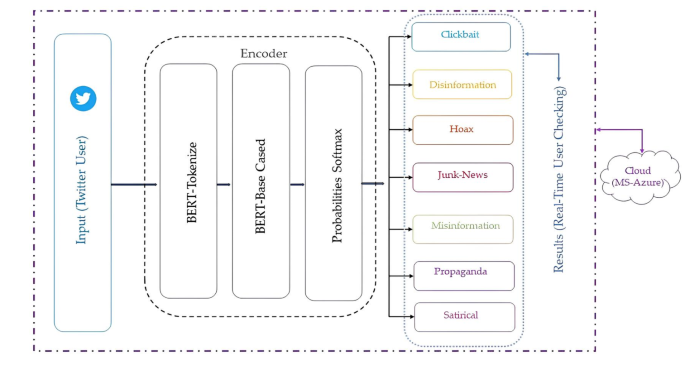
To address these shortcomings, researchers have developed the Fake News Detection on Cloud (FANDC) system—a cloud-based solution designed to detect and categorize fake news in real-time. Unlike previous approaches, FANDC categorizes potential misinformation into seven distinct subcategories: clickbait, disinformation, hoaxes, junk news, misinformation, propaganda, and satire.
The system leverages the Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT) algorithm, which has demonstrated significant success in Natural Language Processing applications. By hosting the system on cloud infrastructure, the developers have created a more secure environment resistant to cyber threats.
“What makes FANDC unique is its ability to not just flag potential fake news, but to provide users with context about what kind of misleading content they’re encountering,” noted one of the researchers involved in the project. “This granular approach helps users make better-informed decisions about what they’re reading and sharing.”
Current fake news detection approaches fall into several categories. Manual verification sites like Turkey’s Teyit.org employ human experts to fact-check content—a process that is thorough but slow, expensive, and unable to scale to the volume of content online. Automated systems using content analysis, linguistic patterns, or network behavior offer faster alternatives but face challenges with evolving deception tactics.
Content-based methods examine the actual text of news items, while language-style approaches look for linguistic patterns common in deceptive content. Source-based detection focuses on identifying known purveyors of misinformation, and propagation-based methods track how content spreads across networks, particularly through bot accounts.
According to researchers, none of these approaches is sufficient on its own. “Detecting fake news requires a multi-faceted approach,” explained one expert. “Malicious actors continuously adapt their tactics, making any single detection method vulnerable to circumvention.”
The FANDC system addresses these limitations through its comprehensive, cloud-based approach, providing real-time feedback to users while maintaining security through distributed computing structures. This represents a significant advance over experimental systems that function only in laboratory conditions with pre-labeled datasets.
As social networks continue to dominate information ecosystems worldwide, the battle against misinformation becomes increasingly crucial. Systems like FANDC point toward a future where technology not only identifies potential falsehoods but helps users understand the nature of the misleading content they encounter.
For platform operators and policymakers, such technological solutions may prove essential in maintaining information integrity while preserving the openness that makes social networks valuable. The challenge remains balancing effective intervention against misinformation with respect for free expression—a balance that technology alone cannot determine.
Fact Checker
Verify the accuracy of this article using The Disinformation Commission analysis and real-time sources.



9 Comments
The COVID-19 pandemic has shown just how damaging the spread of misinformation can be. This technology could play a critical role in protecting public health and safety during future crises.
Absolutely. Timely detection of fake news related to public health emergencies could save lives.
This is an important development in the fight against misinformation. Detecting fake news in real-time could help curb the spread of harmful propaganda and restore trust in online platforms.
Fact-checking and source verification are crucial in an era of information overload. This tool could help social media users make more informed decisions about the content they consume and share.
Impressive work. Leveraging AI and machine learning to identify misinformation in real-time is a significant technical challenge. I’m curious to see how this system performs in the real world.
While this is a positive step, we must remain vigilant. Malicious actors will likely adapt their tactics to evade detection. Ongoing refinement and monitoring of this system will be essential.
I’m curious to learn more about the technical details of this system. How does it differentiate between legitimate news and intentionally misleading content? What are the potential limitations or biases?
Combating misinformation is crucial, especially in the digital age where false narratives can quickly go viral. This technology could be a valuable tool for social media companies and fact-checkers.
Agreed. Rapid detection and removal of fake news is key to maintaining the integrity of online discourse.